Solar energy harnesses energy from the sun, converting it into thermal or electrical energy. It is the most abundant, clean, and renewable energy source available, offering a sustainable way to generate electricity and heat. Solar energy, derived from the sun’s radiation, plays a key role in reducing environmental impact while meeting growing energy demands
Key Points about Solar Energy:
Source: Solar energy originates from sunlight. The sun emits light and heat through nuclear fusion, and solar technologies capture this energy to produce electricity or heat.
- Conversion:
- Photovoltaic (PV) Cells: These are used in solar panels to convert sunlight directly into electricity. When sunlight hits the solar panels, it excites electrons in the photovoltaic cells, generating an electric current.
- Solar Thermal Systems: These systems use sunlight to produce heat, which can be used to heat water or air for homes, or drive turbines to generate electricity.
- Applications:
- Residential and Commercial Power: Solar panels are installed on rooftops or in open spaces to generate electricity for homes and businesses.
- Solar Farms: Large-scale solar energy plants that contribute to the electrical grid.
- Heating: Solar thermal energy is used for water heaters, space heating, and even in industrial processes.
- Advantages:
- Renewable: Solar energy is inexhaustible as long as the sun exists.
- Environmentally Friendly: It does not produce pollution or greenhouse gases during its operation.
- Cost-effective: After installation, solar power reduces electricity bills and can even allow users to sell excess electricity back to the grid.
- Energy Independence: Solar systems allow users to generate their own power, reducing reliance on external energy sources.
- Challenges:
- Intermittency: Solar energy is not constant, as it depends on the sun shining. It requires energy storage systems or backup power sources.
- Space Requirements: Large amounts of land or rooftop area are needed for significant power generation.
- Initial Cost: Installation of solar systems can be expensive, though costs have been declining in recent years.
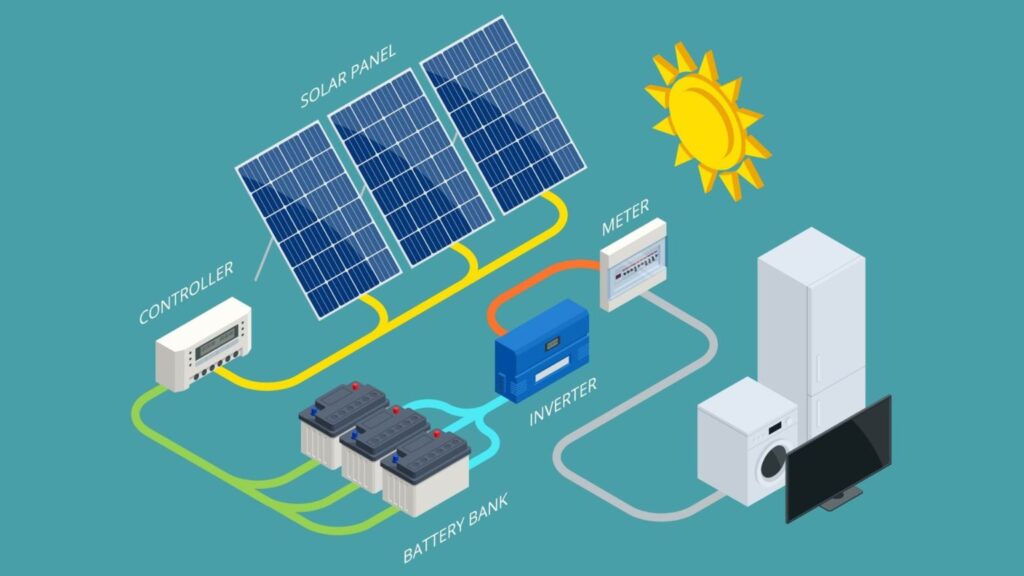
Solar energy is the radiant light and heat from the sun that is harnessed using various technologies to generate electricity, provide heating, and support other energy needs. Here’s an in-depth look at how solar energy works and its benefits:
1. How Solar Energy Works
Solar energy is captured using solar panels or photovoltaic (PV) cells. These cells convert sunlight directly into electricity. The process works as follows:
- Solar cells contain semiconductors, typically made of silicon, that absorb sunlight.
- When sunlight hits these cells, it knocks electrons loose from their atoms, generating an electrical current.
- This direct current (DC) electricity is then converted into alternating current (AC) using inverters, as most homes and businesses use AC electricity.
Another method, known as solar thermal energy, captures sunlight to produce heat, which can be used to heat water or spaces or generate electricity through steam turbines.
2. Types of Solar Energy Systems
- Photovoltaic Systems (PV): Convert sunlight directly into electricity using solar cells. These are the most common systems used for residential and commercial solar energy production.
- Solar Water Heating: Uses solar collectors to heat water for domestic use, reducing the need for gas or electric heaters.
- Concentrated Solar Power (CSP): Uses mirrors or lenses to concentrate sunlight into a small area to produce heat, which generates electricity through a steam turbine.
3. Benefits of Solar Energy
- Renewable and Abundant: Solar energy is a renewable resource, meaning it won’t run out, and it’s available everywhere, even on cloudy days, although with varying intensity.
- Environmentally Friendly: Solar energy doesn’t produce greenhouse gases or pollution during operation, making it a clean energy source. It’s a critical technology in reducing carbon emissions and fighting climate change.
- Cost Savings: While the initial investment in solar panels can be high, solar energy can significantly reduce electricity bills over time. In some cases, excess energy can be sold back to the grid, generating income.
- Low Maintenance: Solar panels typically require little maintenance after installation, as they have no moving parts and can last 25-30 years or more.
- Energy Independence: By harnessing solar power, individuals and countries can reduce their reliance on fossil fuels and energy imports.
4. Challenges of Solar Energy
- Intermittency: Solar energy production is dependent on sunlight, meaning it can’t generate electricity at night or during cloudy weather. This necessitates the use of energy storage systems like batteries.
- Space Requirements: To generate significant power, solar panels require a large surface area, which can be a challenge in densely populated areas.
- Initial Costs: While costs have decreased significantly in recent years, the upfront cost of purchasing and installing solar panels can still be prohibitive for some.
5. Advances in Solar Energy
- Improved Efficiency: Ongoing research is making solar cells more efficient, meaning they can convert more sunlight into electricity.
- Solar Batteries: Energy storage technologies, such as lithium-ion batteries, are becoming more advanced, allowing users to store solar energy for use at night or during cloudy days.
- Solar Farms: Large-scale solar farms are being developed to generate solar energy on a massive scale, contributing to national grids and helping meet renewable energy targets.
If you’re looking for the best solar energy products, Explore below and save money
Solar Power System and Solar Power Products
How Much cost effective is Solar Energy?
While payback time is a good indicator of savings potential, for a complete picture you need to compare your solar savings to other low-risk ways you could have invested your money over the time horizon that is important to you. The following table shows the annual after-tax rate of return you would need to earn on the alternate investment for it to match your solar savings, for three typical payback times:
| 4-year payback time | 6-year payback time | 8-year payback time |
10-year planning horizon | 10.8% | 6.4% | 3.4% |
20-year planning horizon | 9.7% | 7.5% | 6.0% |
*2.5% annual inflation, no cost for maintenance, no effect on insurance, no increase in resale value.
When the payback time is less than 10 years, most homeowners find that an investment in solar power is financially more attractive than any other low-risk investment they could make over the time horizon that’s important to them. Disclaimer